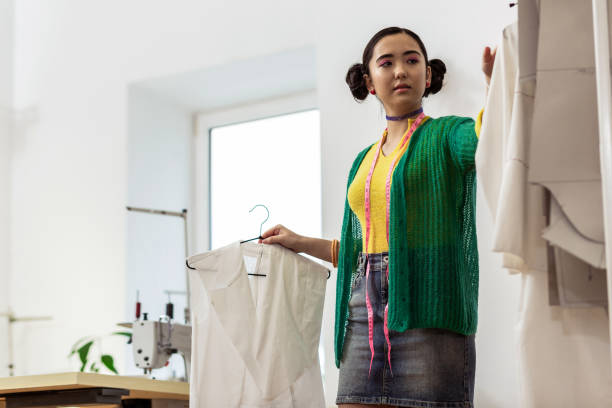
Sustainable fashion has gained significant traction in recent years as consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental impact of the fashion industry. From the use of eco-friendly materials to ethical production practices, sustainable fashion aims to reduce the negative effects of clothing production and consumption on the planet. This article explores the principles of sustainable fashion, the challenges the industry faces, and the future of eco-friendly clothing.
The Environmental Impact of Fashion
The fashion industry is one of the largest polluters in the world, responsible for significant carbon emissions, water consumption, and waste. The rise of fast fashion, characterized by the rapid production of cheap, trendy clothing, has exacerbated these issues. Fast fashion relies on a linear model of take, make, and dispose, leading to a culture of overconsumption and waste.
The production of textiles, particularly synthetic fibers like polyester, is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels. Additionally, the dyeing and finishing of fabrics often involve toxic chemicals that can pollute water sources. The environmental impact extends to the end of a garment’s life, with millions of tons of clothing ending up in landfills each year.
Principles of Sustainable Fashion
Sustainable fashion seeks to address these environmental and social issues by promoting practices that are kinder to the planet and people. Key principles of sustainable fashion include:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Sustainable fashion prioritizes the use of organic, recycled, and biodegradable materials. Organic cotton, hemp, bamboo, and Tencel are examples of natural fibers that are grown without harmful pesticides and use less water. Recycled materials, such as polyester made from plastic bottles, help reduce waste and the demand for virgin resources.
- Ethical Production: Sustainable fashion emphasizes fair labor practices, ensuring that workers are paid fair wages and work in safe conditions. This contrasts with the exploitative labor practices often found in fast fashion supply chains. Brands that adhere to ethical production standards are transparent about their manufacturing processes and often work with certified factories.
- Reducing Waste: Sustainable fashion aims to minimize waste throughout the production process and promote a circular economy. This includes designing garments that are durable and timeless, encouraging consumers to buy less but better quality, and creating systems for recycling and upcycling old clothing.
- Local and Small-Scale Production: Supporting local artisans and small-scale producers is another aspect of sustainable fashion. This approach reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and helps preserve traditional crafts and techniques.
Challenges in Sustainable Fashion
Despite its growing popularity, sustainable fashion faces several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the higher cost of sustainable materials and ethical production, which can make eco-friendly clothing more expensive than fast fashion. This price difference can be a barrier for consumers who are used to the low prices of fast fashion.
Another challenge is the issue of greenwashing, where brands falsely claim to be sustainable to capitalize on the trend. This can make it difficult for consumers to identify truly sustainable brands and products. Transparency and third-party certifications are essential in addressing this issue and building trust with consumers.
Additionally, scaling sustainable practices across the global fashion industry is a complex task. The fashion supply chain is vast and interconnected, making it difficult to implement sustainable practices uniformly. However, as more brands and consumers demand change, the industry is slowly moving towards more sustainable practices.
The Role of Consumers in Sustainable Fashion
Consumers play a crucial role in driving the sustainable fashion movement. By making more conscious choices, such as buying less, choosing quality over quantity, and supporting sustainable brands, consumers can help reduce the environmental impact of fashion. Educating oneself about the impact of clothing production and the importance of sustainability is the first step towards making more informed decisions.
Secondhand shopping, renting clothes, and participating in clothing swaps are other ways consumers can reduce their fashion footprint. These practices extend the life of garments and reduce the demand for new clothing, ultimately helping to lessen the environmental impact of fashion.
The Future of Sustainable Fashion
The future of sustainable fashion looks promising, with innovation playing a key role in driving change. New technologies, such as 3D printing and biofabrication, are being explored to create sustainable materials and production methods. For example, lab-grown leather and fabrics made from mushroom mycelium offer alternatives to traditional textiles that are more environmentally friendly.
As sustainability becomes a priority for more consumers, brands are being pressured to adopt greener practices. The rise of the slow fashion movement, which advocates for a more thoughtful and sustainable approach to fashion, is also contributing to the shift away from fast fashion.
Conclusion
Sustainable fashion is not just a trend; it is a necessary response to the environmental and social challenges posed by the fashion industry. While there are challenges to overcome, the movement towards eco-friendly clothing is gaining momentum, driven by consumers, brands, and innovators committed to creating a more sustainable future. By embracing the principles of sustainable fashion, we can reduce the impact of our clothing choices on the planet and contribute to a more ethical and responsible fashion industry.